Hoverboards have taken the world by storm, offering a futuristic mode of transportation that seems to defy gravity. But have you ever wondered how these sleek, self-balancing devices actually work? In this article, we’ll delve into the science behind hoverboards, exploring the intricate mechanics that make them glide effortlessly. So, fasten your seatbelts, or rather, tighten your helmet straps, as we embark on a journey through the inner workings of hoverboards.
What Is a Hoverboard?
At first glance, a hoverboard may appear deceptively simple, but it’s a sophisticated machine composed of several essential components:

- Gyroscope and Accelerometer: The heart of a hoverboard lies in its gyroscopes and accelerometers. These sensors constantly monitor the device’s orientation and tilt. By analyzing this data, the onboard computer makes split-second adjustments to maintain balance.
- Battery: Most hoverboards are powered by lithium-ion batteries, which store and provide the necessary electricity to drive the motors. These batteries are rechargeable and store a substantial amount of energy.
- Motors: Typically, hoverboards feature two electric motors, one for each wheel. These motors are responsible for propelling the device forward, backward, and turning left or right. The power to each motor is controlled independently, allowing for precise maneuverability.
- Logic Board: The logic board, often referred to as the “brain” of the hoverboard, interprets data from the sensors and sends instructions to the motors. It ensures that the device remains level and responds to rider input.
- Footpads: The rider’s feet rest on the footpads, which house pressure-sensitive switches. When the rider leans forward or backward, these switches detect the change in pressure and signal the logic board to adjust the motors accordingly.
| Component | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Gyroscope and Accelerometer | Balance Control | These sensors continuously monitor the device’s orientation and tilt, sending data to the logic board for balance adjustments. |
| Battery | Power Source | Lithium-ion batteries store and provide electricity to drive the motors. |
| Motors | Propulsion | Typically, hoverboards have two electric motors (one for each wheel) for forward, backward, and turning motion. |
| Logic Board | Control Center | The logic board interprets data from sensors and instructs the motors to maintain balance and respond to rider input. |
| Footpads | User Interface | Pressure-sensitive switches in the footpads detect rider movements and provide input to the logic board. |
These components work together seamlessly to create a self-balancing and maneuverable hoverboard, making it an innovative and enjoyable mode of transportation.

How Does It Stay Balanced?
The key to a hoverboard’s stability is its ability to maintain equilibrium, even when a rider leans forward or backward. This is where the gyroscopes and accelerometers come into play. When a rider leans forward, the sensors detect the change in angle and instruct the motors to rotate the wheels in the appropriate direction to counteract the movement. This continuous adjustment process keeps the hoverboard balanced, making it seem as though it’s floating effortlessly.
How Does It Move?
Hoverboards move by precisely controlling the rotation of their wheels. To move forward, both wheels rotate in the same direction at the same speed. To turn, one wheel spins faster than the other, causing the hoverboard to pivot in the desired direction. When you lean forward, the sensors detect the shift in weight and signal the motors to engage, propelling the device forward. Leaning backward has the opposite effect, causing the hoverboard to reverse.
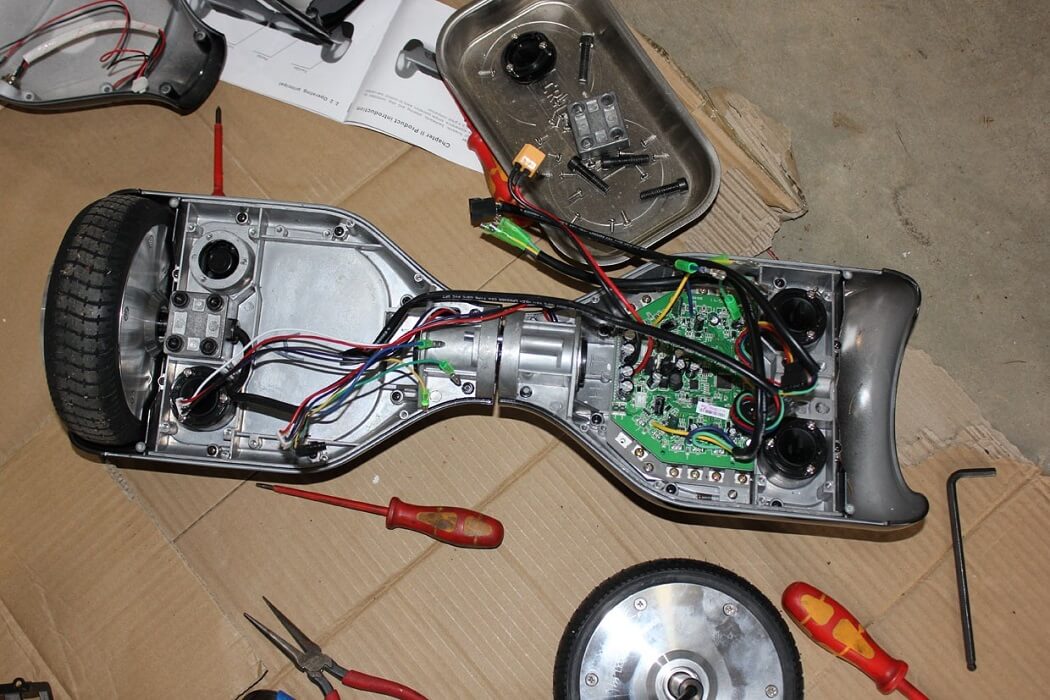
Battery Power
The battery in a hoverboard supplies electricity to the motors and logic board. The voltage from the battery is converted into the current needed to power the motors, allowing the hoverboard to move. The size and quality of the battery affect the device’s range and performance. It’s crucial to use a charger designed for your specific hoverboard model and follow safety guidelines to prevent battery-related issues.
Hoverboard Facts
- Not Actual Hoverboards: Despite the name, hoverboards do not actually hover. They have wheels and make contact with the ground, relying on self-balancing technology.
- Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Scooters: Hoverboards are essentially self-balancing scooters with two wheels. They were first introduced to the market in the early 2010s.
- Electric-Powered: Hoverboards are powered by electric motors, typically powered by rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. These batteries provide the energy needed to move the device.
- Gyroscope and Accelerometer: Hoverboards are equipped with gyroscopes and accelerometers that constantly monitor the rider’s balance and movement. These sensors play a crucial role in keeping the device stable and responsive.
- Learn to Move: To control a hoverboard, riders lean forward to move forward, lean backward to move backward, and lean to the sides to turn. The sensors and motors work together to interpret and execute these movements.
- Top Speed: The top speed of a hoverboard varies depending on the model but typically ranges from 6 to 12 miles per hour (10 to 20 kilometers per hour).
- Range: Hoverboards have a range of about 10 to 20 miles (16 to 32 kilometers) on a single charge, though this can vary based on factors like rider weight, terrain, and speed.
- Charging Time: Charging a hoverboard usually takes 2 to 3 hours to reach a full charge. It’s important to use the manufacturer’s recommended charger to prevent battery issues.
- Safety Concerns: Hoverboards gained notoriety for safety concerns related to battery fires and malfunctions in some early models. Safety standards have since improved, and it’s essential to purchase from reputable brands with certified batteries.
- Popularity: Hoverboards gained popularity quickly, with celebrities and influencers showcasing them on social media. However, regulations and laws regarding their use vary by location, and some places have restricted or banned them in certain areas.
- Variety of Models: There are various types of hoverboards available, including off-road models with larger, sturdier wheels for rough terrain and smaller, more compact models for urban use.
- Learning Curve: Riding a hoverboard can take some practice, as it requires a sense of balance and coordination. Most riders become proficient after a short period of practice.
- Age and Weight Limits: Manufacturers often specify minimum and maximum rider weight limits, as well as recommended age ranges for safe use.
- Accessories: Hoverboard accessories, such as protective gear (helmets, knee pads, and elbow pads), carrying bags, and Bluetooth speakers, are available to enhance the riding experience.
- Legal Considerations: It’s important to check local regulations and laws regarding the use of hoverboards, as they may be treated differently in various regions and may have specific restrictions.

Remember that hoverboard technology continues to evolve, and new features and safety enhancements are constantly being introduced to the market. When using a hoverboard, safety should always be a top priority, and riders should follow manufacturer guidelines and exercise caution to prevent accidents or injuries.
Conclusion
Hoverboards may seem like magical, self-balancing transportation devices, but their operation is rooted in the principles of physics and engineering. Through a combination of sensors, motors, and clever algorithms, hoverboards can maintain balance and respond to rider input with remarkable precision. Understanding the science behind hoverboards not only enhances our appreciation for these innovative gadgets but also underscores the importance of safe and responsible riding practices. So, the next time you step onto a hoverboard, remember that beneath your feet lies a world of science and technology that makes the seemingly impossible, possible.
How Does a Hoverboard Work Video Review
FAQ
Q: What is the basic principle behind how hoverboards work?
A: Hoverboards use a combination of sensors, such as gyroscopes and accelerometers, to detect the rider’s balance and movement. They then adjust the speed and direction of the electric motors in the wheels to maintain balance and respond to rider input.
Q: Do hoverboards actually hover above the ground?
A: No, hoverboards do not hover above the ground like the ones you might have seen in science fiction movies. They have wheels and make contact with the ground, relying on self-balancing technology to stay upright.
Q: How does a hoverboard know when to move forward, backward, or turn?
A: Hoverboards move in response to the rider’s movements. Leaning forward makes the hoverboard move forward, leaning backward makes it go backward, and leaning to the sides initiates turning. The onboard sensors detect these shifts in weight and send signals to the motors to execute the corresponding actions.
Q: What powers a hoverboard?
A: Hoverboards are powered by rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. These batteries store and provide the necessary electrical energy to drive the electric motors.
Q: How fast can a hoverboard go?
A: The top speed of a hoverboard varies by model, but it typically ranges from 6 to 12 miles per hour (10 to 20 kilometers per hour). Some high-performance models may reach slightly higher speeds.
Q: How far can a hoverboard travel on a single charge?
A: The range of a hoverboard depends on factors like rider weight, terrain, and speed. On average, most hoverboards have a range of about 10 to 20 miles (16 to 32 kilometers) on a single charge.
Q: How long does it take to charge a hoverboard fully?
A: Charging time varies, but it typically takes 2 to 3 hours to fully charge a hoverboard battery. It’s essential to use the manufacturer’s recommended charger to prevent battery issues.
Q: Are hoverboards safe to ride?
A: Hoverboards can be safe when used responsibly and on appropriate surfaces. However, there were safety concerns in the past related to battery fires and malfunctions in some early models. Choosing a reputable brand with certified batteries and following safety guidelines is crucial for safe riding.
Q: Are there age and weight limits for riding hoverboards?
A: Manufacturers often specify minimum and maximum rider weight limits, as well as recommended age ranges for safe use. It’s important to adhere to these guidelines for a safe riding experience.
Q: Do I need protective gear when riding a hoverboard?
A: Wearing protective gear such as helmets, knee pads, and elbow pads is highly recommended, especially for beginners. Safety gear can help prevent injuries in case of falls or accidents.
Q: Can I use a hoverboard legally in my area?
A: The legality of hoverboard use varies by location. Some places have specific regulations and restrictions, such as where and how you can ride them. It’s essential to check your local laws and regulations regarding hoverboard use to ensure compliance.










